
- #Dna coloring transcription and translation how to
- #Dna coloring transcription and translation full
- #Dna coloring transcription and translation code
- #Dna coloring transcription and translation series
#Dna coloring transcription and translation code
Only certain segments of this gene actually code for amino acids. The entire sequence of nucleotides in the entire template strand is transcribed into a primary RNA transcript. Therefore, triplet codes and codons are analogous in function. In DNA the three base sequences are called triplet codes, while in RNA the three bases sequences that specify one amino acid are called codons. The tail is vital in that it gives the signal necessary to allow the RNA to move out of the nucleus and then bind to ribosomes in the cytoplasm where proteins will be synthesized from the encoded information.
#Dna coloring transcription and translation series
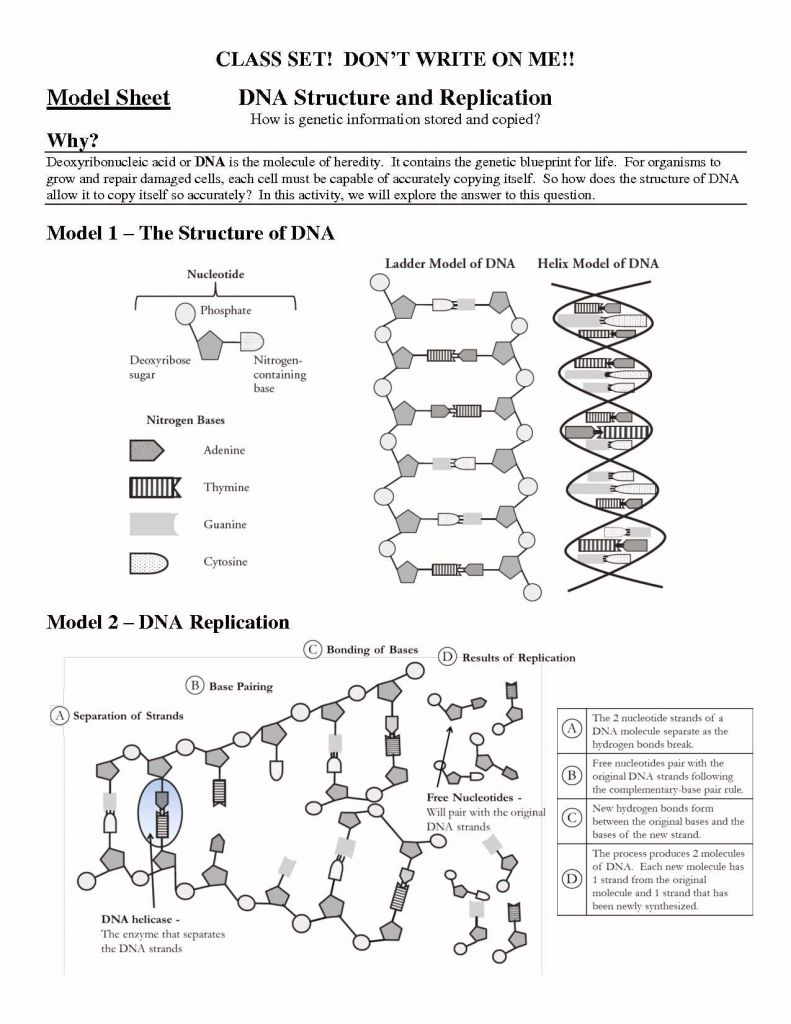
As a final touch, a series of adenine nucleotides called the poly A tail is added to the end of the transcribed RNA strand. When the triplet codes reach a stop sequence or stop signal, the RNA polymerase ends the chain and releases then RNA transcript. RNA polymerase is the enzyme that joins together the aligned ribonucleotides into a strand. The sequence is located near the beginning of the gene. The template strand is determined by the presence of a specific sequence of DNA nucleotides called the promoter. One of the strands will act as a template and will determine the sequence of RNA nucleotides. The first item of business in protein synthesis is the unraveling of the DNA double helix and separation of the two strands of nucleotides. Protein Synthesis Transcription: mRNA synthesis The genetic code is universal in all cells. As the triplet codes are read, the appropriate amino acid is added to the growing chain, the final result being a protein as determined by the DNA information. Sixty-one (61) of the codes are matched up to one of the 20 amino acids, a given amino acid can be specified by more than one triplet code, while the remaining three triplet codes act as stop signals and end the protein chain rather than adding an amino acid. The 4 bases can be arranged into 64 different triplet codes (sequence of three bases). Recall that there are 4 bases in DNA (Guanine, adenine, cytosine, thymine) and 20 amino acids that are linked together in different arrangements to make various proteins. Each triplet code is ‘read’ and calls for a specific amino acid. A triplet code is a sequence of three bases along a single strand of DNA.
Recall that DNA nucleotides are composed of long chains of bases. RNA molecules themselves are synthesized according to the information coded in DNA. You can change the color scheme by clicking on the gear icon and selecting the wrench icon next to Coloring Scheme.RNA molecules are responsible for transferring information from DNA to the site of protein synthesis. Polarity: Colors indicate specific polarities: Hydrophobicity: The residues are colored on a spectrum from red to blue, where red means hydrophobic and blue means hydrophilic. In general, polar residues are brighter colors, while non-polar residues appear more subdued. RasMol: This coloring scheme is traditional, and groups amino acids by property.
The default color scheme in Benchling is RasMol, however, Benchling supports three color schemes: If the translation corresponds to a non-standard genetic code, an AA sequence identical to the translation and its non-standard genetic code will be created. Select a folder, a new name, and a schema for the AA sequence. Right-click the translation and select Create AA Sequence. To create an amino acid sequence map from a translation on a DNA or RNA sequence: On the Features panel click the Create New at the top of the panel.Īlternatively, you can select a region or an annotation on the sequence, right-click, and select Create TranslationĮnter the translation name, genetic code, strand direction, notes, and custom fields.Ĭreate an amino acid sequence from a translationĬreating separate amino acid entities enables customized protein-specific viewing options such as color scheme, CDR annotations, and liability sites. Highlight your region of interest or annotation on the DNA.

To create a translation for a DNA or RNA sequence:
#Dna coloring transcription and translation full
This opens a full list of translations in a Translations tab where you can more easily view and manage them. You can view all the translations on a sequence in a larger window by clicking Show Expanded View in the Features panel. To access the Features panel, click the flag icon in the right-side menu. Access the translations listĬreate, view, and delete annotations in the Features panel and its expanded view.
#Dna coloring transcription and translation how to
This article goes over how to access the translations list, and from there, create, analyze, and add to translations. You can translate DNA and RNA sequences, create amino acid (AA) sequences, and generate biochemical properties for translations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
